 |
Aquatic Invasive Species

Rusty Crayfish (Faxonius rusticus)
What is a Rusty Crayfish?
Rusty Crayfish (Figure 1.) is a species of crayfish not native to Canada. They are native to the Ohio River Basin in the United States.

Figure 1. A Rusty Crayfish. Photo credit: D. Watkinson, Government of Canada
Why are they an issue?
Rusty Crayfish are a concern to Manitoba because they:
- can severely reduce aquatic vegetation, depriving native fish of cover, spawning habitat and food
- harm native fish populations by consuming their eggs and young
- are aggressive and able to avoid predation by fish
- are prolific spawners
- can reduce and displace native crayfish
- can hybridize with native crayfish
Experience from other North American watersheds - especially those with larger-sized water bodies - indicate that once AIS establish, they are cost prohibitive to eradicate.
Prohibition
Rusty Crayfish are designated as an aquatic invasive species (AIS) in Manitoba.
It is illegal to:
- possess a member of an AIS in Manitoba
- bring a member of an AIS into Manitoba or cause it to be brought into Manitoba
- deposit or release a member of an AIS in Manitoba or cause it to be deposited or released in Manitoba
- transport a member of an AIS in Manitoba
Where are Rusty Crayfish found in Manitoba?
Rusty Crayfish were found in:
- the Ontario portion of Lake of the Woods in 1990
- the Ontario portion of the Winnipeg River in 2006; they have not been reported in the Manitoban portion of the Winnipeg River
- Falcon Lake in 2007
- a portion of the Birch River near Prawda, Manitoba in 2011
- the Manitoba portion of Lake of the Woods (i.e., Buffalo Bay) in 2021
Distribution of Rusty Crayfish in Manitoba
A Rusty Crayfish distribution map of can be found here.
How did Rusty Crayfish get to Manitoba?
Rusty Crayfish were likely introduced by recreational anglers through an illegal bait bucket release.
How to identify Rusty Crayfish
Rusty Crayfish can be identified by their:
- larger body and claws compared to native species
- brown/olive green body and claws
- rusty colored patches on either side of their carapace in front of the start of their tails
- black tipped, slender claws
- oval gap in claw when closed (see Figure 2. below)
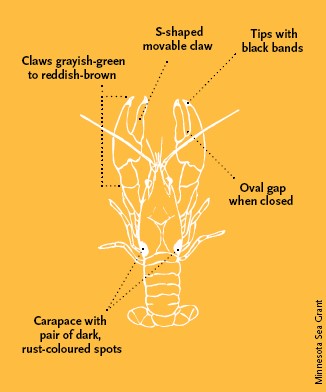
Figure 2. Rusty Crayfish can be identified by the above characteristics. Source: Minnesota Sea Grant.
How to tell the difference between native Northern Crayfish (Faxonius virilis) and a Rusty Crayfish?
|
|
Northern Crayfish claws are usually blue and when closed there is no gap between the upper and lower claw portions (Figure 3.). Rusty Crayfish have an oval gap when their claws are closed (Figure 4.) as well as a rusty patch on their side (Figure 5.).
How to stop the spread of Rusty Crayfish in Manitoba
The most effective prevention is to stop the human-caused movement, introduction and spread of Rusty Crayfish. All surface water-users play a role in preventing the introduction and spread of Rusty Crayfish. Prevention is our best defense.
When Rusty Crayfish were found in Falcon Lake, the Manitoba government created a zero possession limit for crayfish (i.e., no crayfish can be in your possession) in 2008. Due to this requirement, there are no Aquatic Invasive Species Control Zones in place for this species.
Schedule A of the AIS Regulation specifies which crayfish species and in what condition it can be possessed in Manitoba. This stipulation is to allow for human consumption.
The AIS Open-water Season and Winter (Ice-covered) Season checklists are step-by-step resources that can help you prevent the spread of Zebra Mussels and comply with the Manitoba government’s AIS Regulation.
Set fines for AIS offences are in effect year-round.
What should I do if you see an AIS such as Rusty Crayfish?
If you see a Rusty Crayfish in a water body where they are not known to exist, note the location, take pictures and report to the Manitoba government’s AIS Unit by:
- emailing AIS@gov.mb.ca
- calling 1-877-867-2470


